Easy Disk Checker: Disk and Flash Drive Utility
Easy Disk Checker is an easy-to-use Windows utility for working with disks and flash drives at the "physical" level, regardless of the file system or its absence.
The application is designed as a single executable EXE file, requires no installation, leaves no traces in the system, does not install drivers, and does not access the registry. It is ready to work immediately after extraction from the ZIP archive.
2025.03.17 - version 1.1.3 - Added SMART support for USB SCSI SATA drives, expanded the list of known-smart-attributes.
2025.03.21 - version 2.0.0 - Added SMART support for USB SAT12 drives, expanded the list of known-smart-attributes, added detection of logical and physical sector sizes, added write function.
2025.04.18 - version 2.0.1 - Expanded the list of known-smart-attributes.
2025.06.03 - version 2.1.1 - Ability to remove Microsoft Storage Pool (Msft Space Device).
2025.06.08 - version 2.2.0 - Added the ability to view the internal model of external USB drives, improved the HEX Viewer module.
2025.06.14 - version 2.2.1 - Added an exception when checking the internal model for flash drives and memory cards.
2025.09.20 - version 2.3.0 - Reworked and significantly accelerated disk reading and writing, added display of average process speed.
2025.10.04 - version 2.4.1 - Added byte editing function in the HexViewer module.
2025.11.05 - version 2.5.0 - Fixed bugs in determining the internal model of USB drives.
2025.11.23 - version 3.0.0 - Added automatic parsing of logical disk structure with support for auto-detection of NTFS, exFAT, FAT32, FAT16, ReFS, BitLocker, APFS, HFS+, HFS, ext2/ext3/ext4, Btrfs, XFS, LVM PV, LUKS (dm-crypt), UFS1 / UFS2, ISO9660, UDF, and basic ZFS detection.
2025.12.08 - version 4.0.0 - Major update: added automatic OS language detection with automatic and manual interface language switching (rus\eng), added image read\write functions with automatic sleep mode blocking during the process, completely reworked the appearance and functionality of disk read\write test windows, added VID\PID display for USB flash drives and memory cards with auto-detection of microcontroller and memory (database in progress), added detection of Host Protected Area limits and ATA password.
2025.12.11 - version 4.3.0 - Interface change for language switching, improvement of full disk write algorithms, fix for s\n detection error on NVMe drives, improvement of the parser and SMART values output, enhancement of algorithms for working with "generic" USB-SATA and USB-NVMe adapters.
2025.12.15 - version 4.4.0 - Added output of spindle speed information for HDD, added option to check "OZON/Aliexpress flash drives" for fake capacity, added read speed benchmark for the selected drive, added Seagate FARM summary output, SMART indicators moved to a dropdown list.
2026.01.02 - version 4.5.2 - Added automatic search for lost partitions and recreating MBR\GPT records based on findings. Added right-click call for the built-in file explorer with support for Fat16\32\exFAT, NTFS, Ext2\3\4, HFS+ with the ability to view and copy directories and files. Modified image reading mode: added choice between full sector-by-sector copy and VHD\VHDX formats with dynamic expansion support. Improved localization, implemented forced remounting of drives "held" by Windows during flash drive tests, full write tests, and image writing.
2026.01.27 - version 4.6.0 - All image functions are now grouped in a separate window. Added direct disk-to-disk cloning and creation of an image of a single volume (in the logical partitions context menu). Added "Quick Clean" option (removal of all partitions). Changed the HEX editor module, added support for 1251 and UTF-8 encodings, the editor is now accessible via the context menu of the logical partitions window. Improved MBR\GPT analysis. Deep rework of handling situations where Windows prevents changes to a mounted disk.
2026.02.05 - version 4.7.2 - Added separate output for drive temperature values based on SMART. Added option to open an image file with logical partition selection and work with it in the built-in "Explorer". Improved partition recovery function (added selection from found items). The logical structure can now also be opened with a double mouse click. Updated the flash drive controller database, fixed minor bugs.
💻 Supported Hardware:
- USB, NVMe, SATA, and PATA controllers
- Hard Disk Drives (HDD) and SSD (SATA / NVMe)
- External USB drives
- USB flash drives and memory cards
📊 Diagnostics:
- View the drive's logical structure
- Output drive parameters (LBA count, sector size, firmware version, RPM, etc.)
- View S.M.A.R.T. attributes and Seagate FARM logs
- Detect HPA (Host Protected Area) and ATA passwords
- Identify the internal model of external HDDs (bypassing the USB bridge)
- Output VID and PID for flash drives and microcontroller information
- Identify drives participating in Microsoft Storage Spaces
🔬 Testing:
- Surface Test: Full scan for bad blocks (bad sectors)
- Fake Check: Identification of flash drives with fake capacity
- Benchmark: Measurement of average read speed
🛠 Repair:
- Quick Clean: Forced "zeroing" of the MBR record to radically fix any logical problems with the drive*
- Bad Block Fixing: Full sector-by-sector write to fix soft-bads or initialize the built-in defect replacement function where possible
💾 Backup:
- Read and write sector-by-sector disk images without modification (*.bin)
- Create VHD / VHDX dynamic images and "deploy" them to a physical disk
- Create an image of a partition (volume)
- Disk-to-disk cloning
- Open image files in the built-in explorer with an option to extract files and folders*
📤 Data Recovery:
- View and edit HEX content of sectors
- Recover damaged MBR / GPT records for lost or deleted partitions
- View and copy files from FAT, NTFS, exFAT, Linux (Ext2/3/4), and Mac (HFS+) partitions
* - implemented in version 4.7.x
At startup, the interface language is set according to Windows language settings, and a check for a new version is performed, with an offer to download the update if found on the server.
Getting Started and Interface
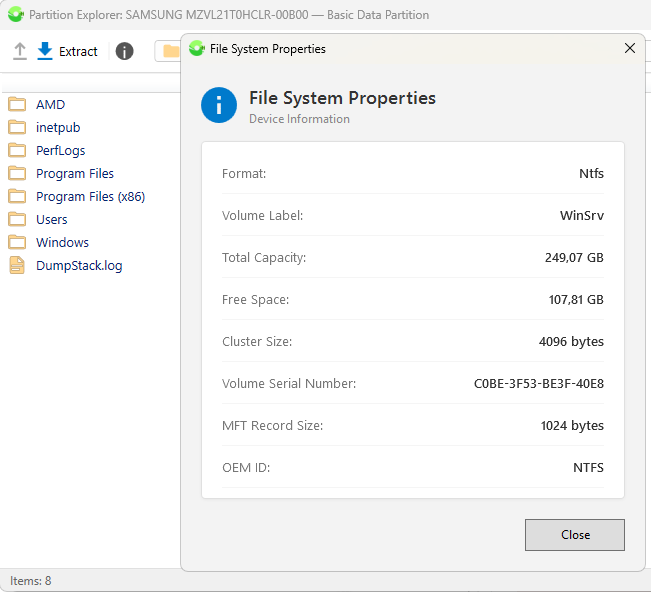
When the program starts, the main window opens with the active "Disk List" button. Clicking it initiates a scan of the buses (SATA, USB, NVMe) and displays a list of physical devices available in the system. For each disk, the model, serial number, firmware version, physical capacity, LBA addressing, and the volume label set in the OS are displayed.
Important: For the program to work correctly (accessing physical devices and reading S.M.A.R.T.), it must be run with Administrator privileges for direct hardware access. The application has limited functionality when running in virtual machines.
When a disk is selected, its logical structure (MBR/GPT partitions, file systems) is displayed at the bottom of the window. In case of a Master Boot Record sector 0 read error, information about the identified problem is displayed.

From here, by right-clicking, you can call the context menu to launch the HEX editor for visual assessment of sector content and editing with saving changes.
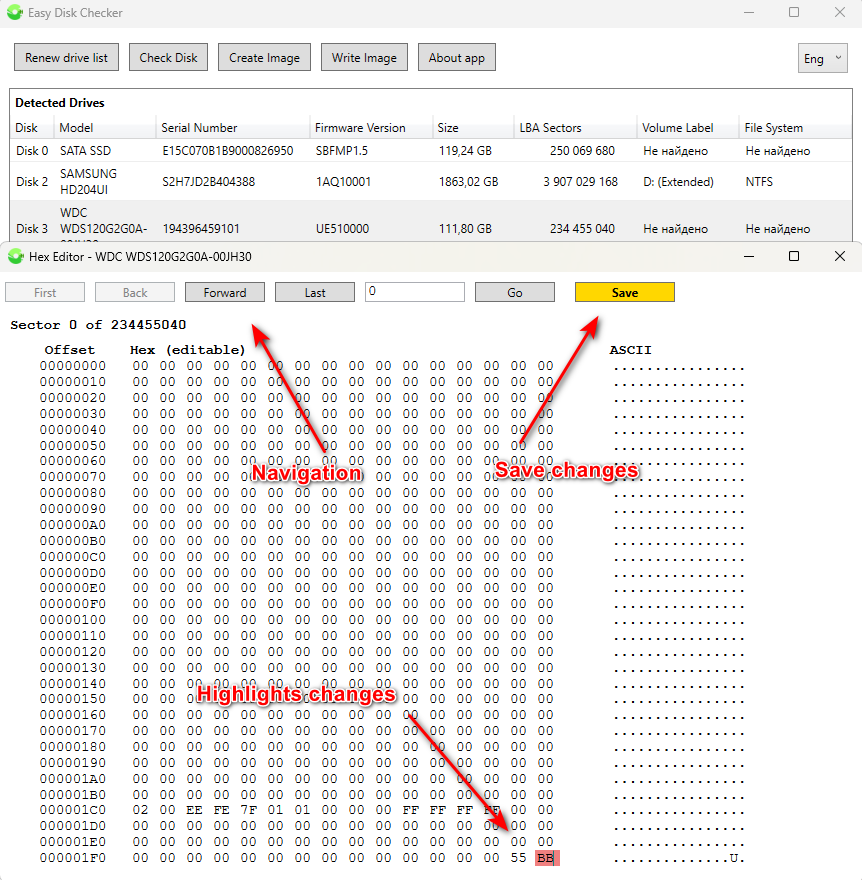
WARNING: Incorrectly modifying data in the HEX editor (e.g., in the partition table or MBR) can lead to the loss of logical partitions and the inability to boot the OS.
Disk Layout Recovery
If selecting a disk automatically detects the absence of a layout due to a logical failure, or accidental or intentional deletion of partitions, the user is offered the option to scan and restore volumes.
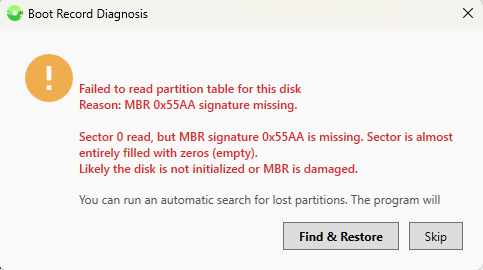
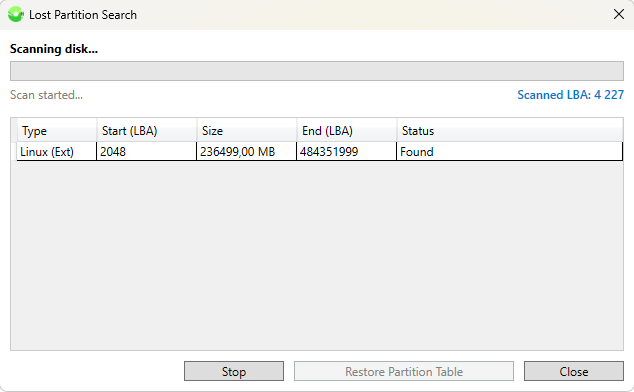
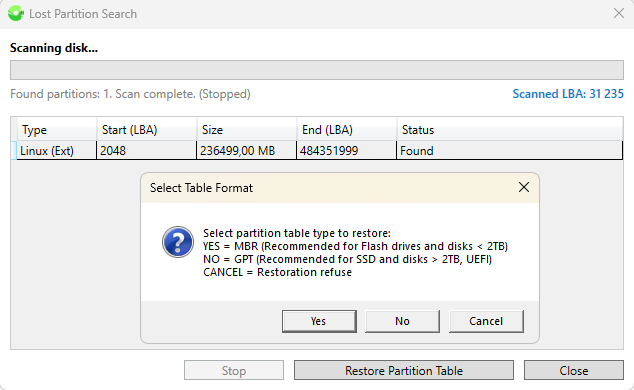
Based on the found partitions, you can form an MBR or GPT layout and gain standard access to files in the found volumes. This function is non-destructive for data, as even in case of incorrect user actions, only the first few sectors of the disk will be written.
Copying Files from Disk Without Mounting
If the layout analysis is successful, recognized partitions with information about their parameters and file system appear in the "Logical structure of the selected disk" window. By right-clicking to call the context menu, you can launch the built-in file explorer to view the contents of the selected partition and copy selected files and folders to a specified location in the "host" system.
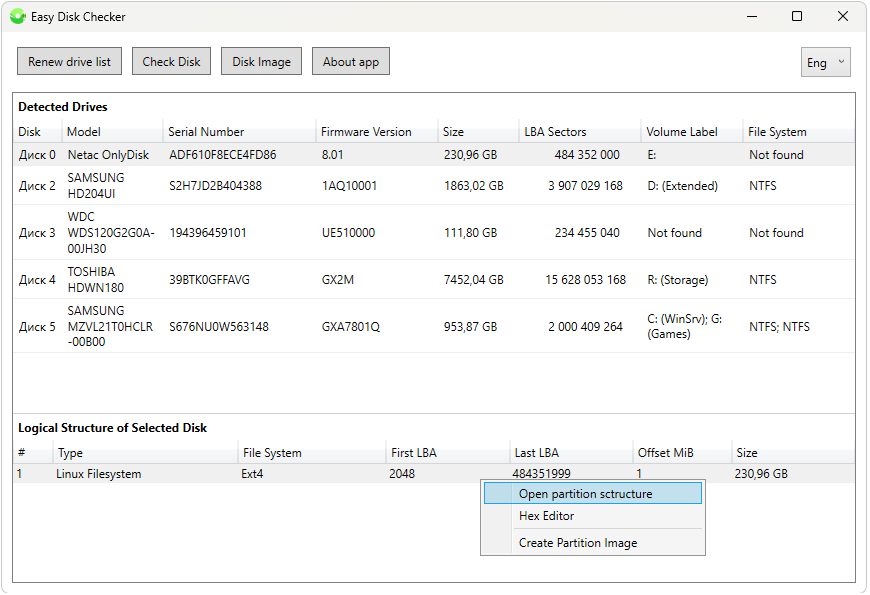
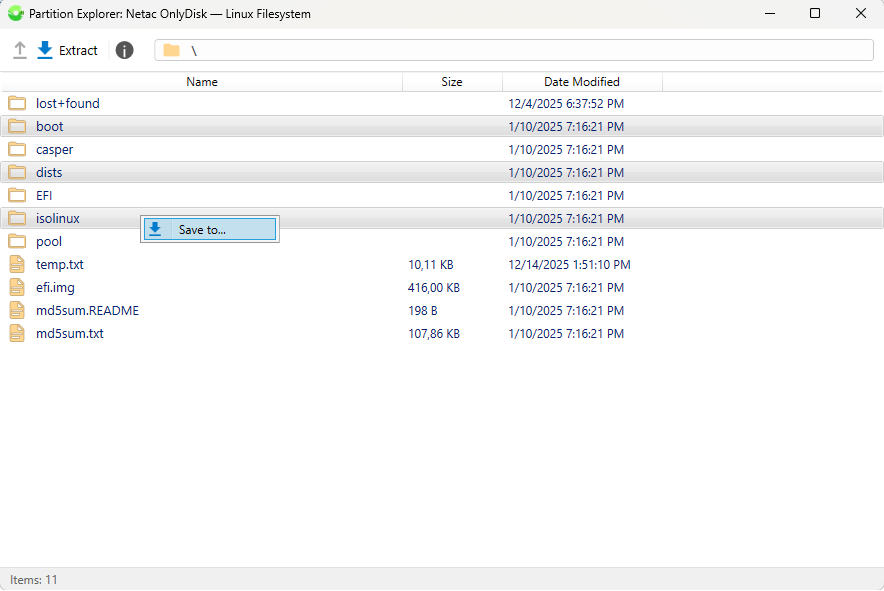
Thus, using Easy Disk Checker, you can bypass the OS to view and copy data for the following file systems: Fat 16\32, ExFAT, NTFS, Ext-2\3\4, HFS+. Additionally, by clicking the icon with an exclamation mark, you can view advanced information about the open volume.
After filling the disk list and selecting a drive, the following buttons become active:
Disk Check
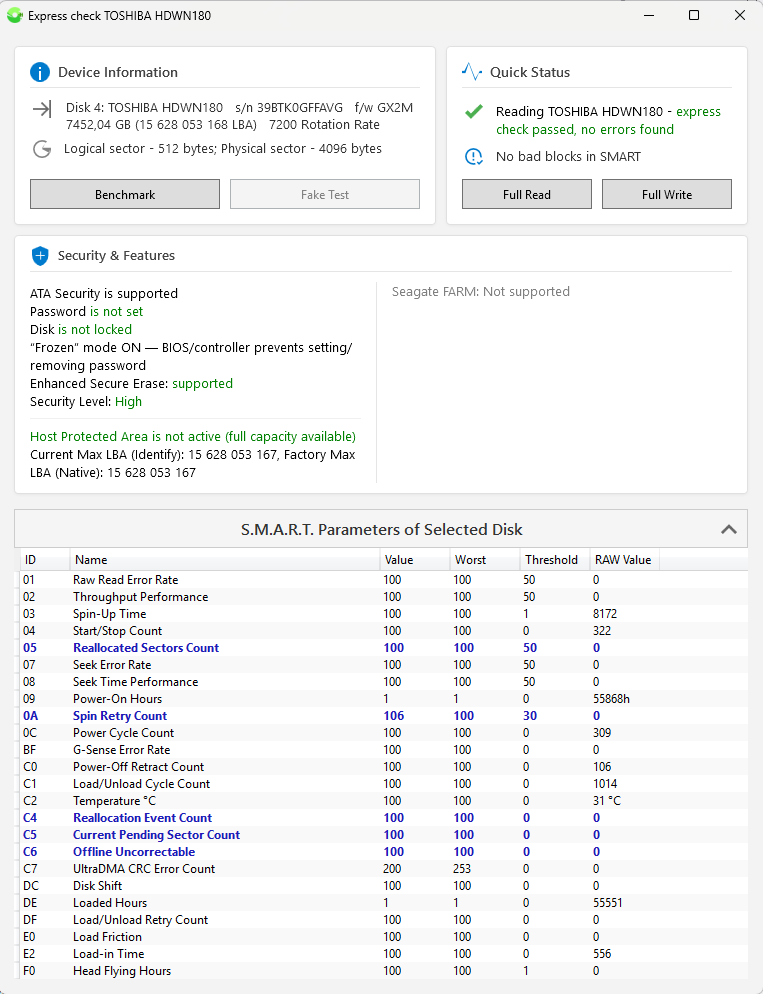
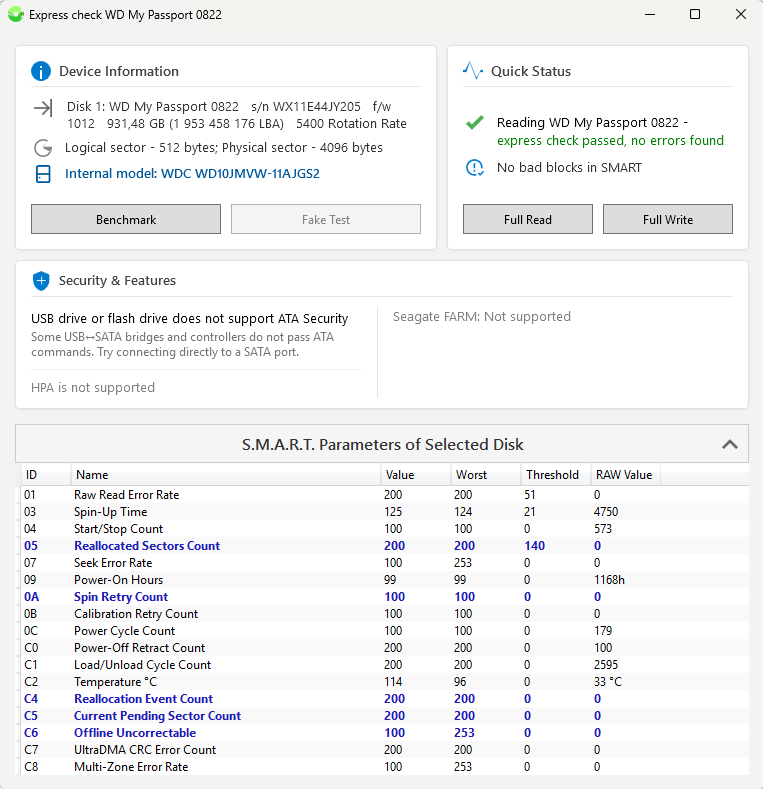
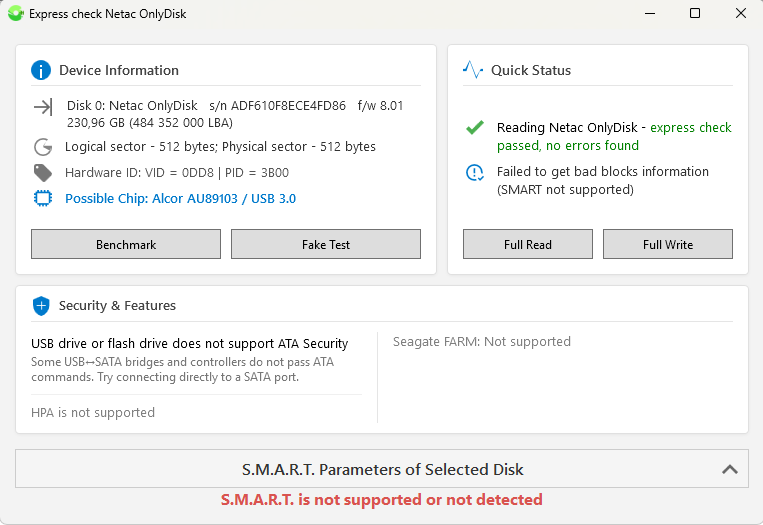
Selecting the required drive in the "Detected Disks" window and clicking "Check Disk" opens a summary information window divided into functional blocks:
- Device Information — model, serial number, firmware version, capacity, and if supported, RPM value, external disk internal model, flash drive VID\PID, assumed microcontroller model (helps in finding service utilities for "flashing"), and buttons:
"Benchmark"
"Fake Test" (available only for flash drives and memory cards). - Current Status — express disk read check in LBA areas at the beginning, middle, and end of the disk, and buttons:
"Full Read"
"Full Write" - Security and Features — if possible, output of ATA password information, HPA (Host Protected Area), and Seagate FARM (available only on modern Seagate drives).
- SMART Self-Test Table Output, collapsed by default, not supported on USB Flash and memory cards.



Working with Images
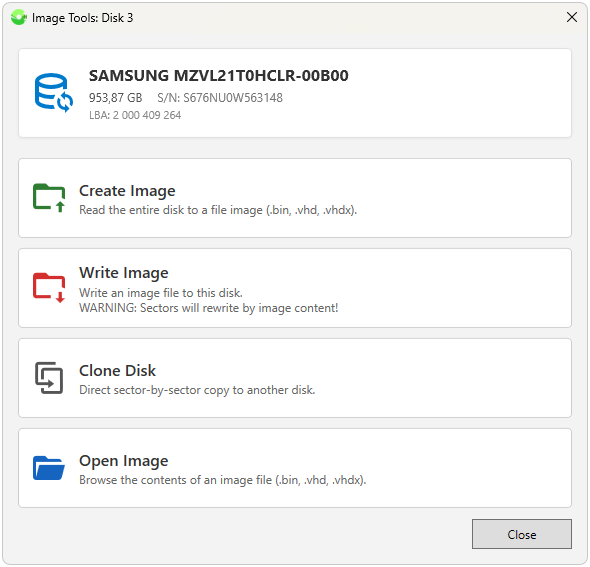
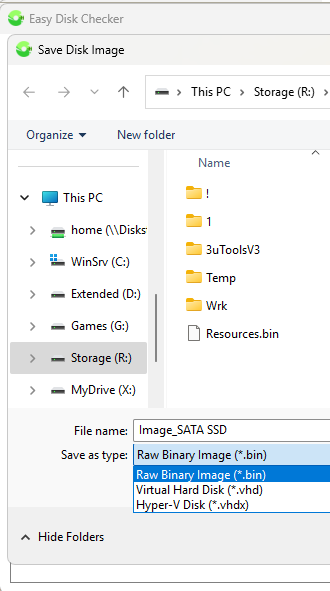
The process creates a full sector-by-sector image of the selected disk without compression or modification (*.bin) or a dynamic image with compression and the ability to mount it in Windows natively (*.vhd *.vhdx). Image files obtained this way can be mounted in Windows as virtual disks natively via the context menu in "Windows Explorer" by right-clicking. Moreover, the size of an image file from a disk where few sectors are occupied by data (filled with zeros) can be several times smaller than the full volume. All that is required is to choose the save path and filename; the extension will be assigned automatically.
Clicking the "Cancel" button interrupts the process; the partially read image file is not deleted. Windows "Sleep Mode" is blocked during reading. Additionally, an option is available to create images in VHD / VHDX format with support for compression and dynamic expansion.


Write Image
Use with care! Writing an image to the selected disk is functionally no different from reading, except that two warning windows are displayed before starting, as incorrectly writing an image to the wrong destination disk will lead to irreversible overwriting of the sectors. Supports both binary image writing and VHD / VHDX deployment.
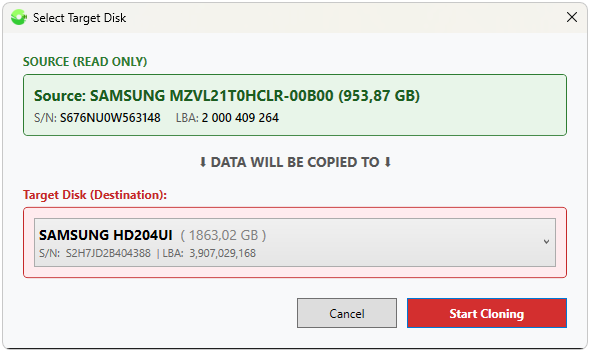
Disk Cloning
Performs a sector-by-sector disk-to-disk transfer; can be used as a backup method for system and work disks, as well as flash drives.
Open Image File
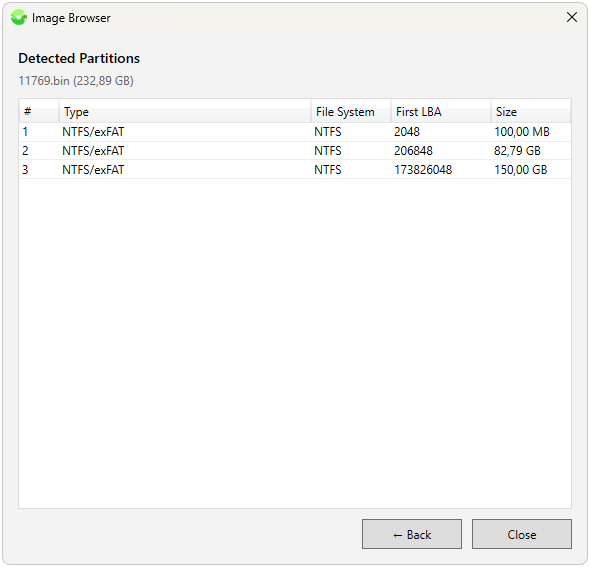
Allows opening any binary image without modification (bin, img, etc.) or a VHD/VHDX image with partition structure detection and opening the partition structure via context menu or double-click in the built-in "Explorer" with multi-select support for saving objects.
Benchmark
Runs four read iterations in different areas of the selected disk, outputting the average calculated speed in MB/s.

Fake Test
Function becomes active if a USB flash drive or memory card is selected.

Used for so-called "Aliexpress flash drives" or OZON drives. The algorithm detects flash drives with artificially inflated capacity. If the actual capacity matches the declared one, it displays a corresponding message:

Full Read
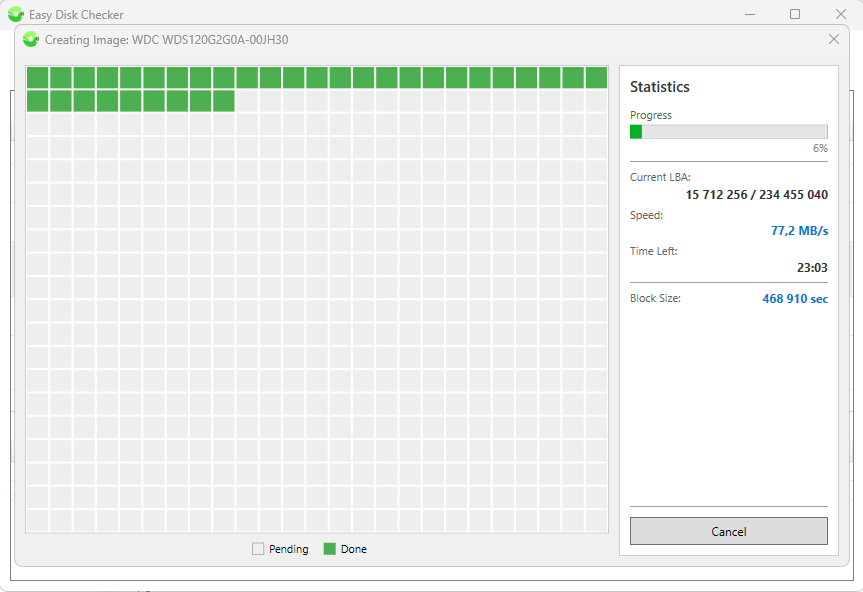
The utility performs a linear read to search for bad blocks and bad sectors, sequentially reading every sector of the disk from beginning to end. For convenience, sectors are grouped into dynamic blocks.
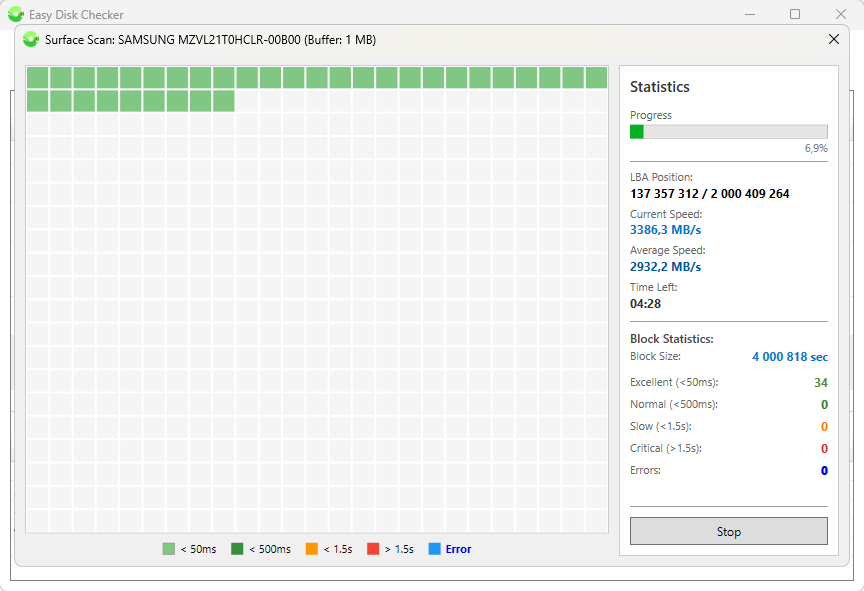
When testing a disk, the block map on the left side of the window is filled according to the legend, while the right side displays information about the automatically selected block size, current sector address, instantaneous and average read speeds, and estimated time until the end of the test.
Full Write
Identical to the read test; a message about irreversible data loss of the overwritten sectors is displayed before the test begins.
WARNING: DESTRUCTIVE FUNCTION! All sectors on the selected disk will be irreversibly overwritten with the 00h pattern.
Running a brief write test can solve issues with the inability to delete a partition using standard Windows tools.
Removing Microsoft Storage Pool (Microsoft Storage Space Device)
Based on requests from colleagues and users, the ability to remove the Microsoft Storage Space Device "flag" (also known as Microsoft Storage Pool) on HDD or SSD has been added. Such structures are created using Windows wizards and cannot be easily fixed via Disk Management.


The key change to the physical structure of the drive is the pool layout written in the second sector (at offset 0x400).

In the case of a pool consisting of two physical disks, it appears in the utility window as two physical disks and one logical virtual structure (MsftStorage Space). To remove it, identify the array disks by matching strings in the MBR analysis window and run a full write test on each, interrupting it after it starts.




